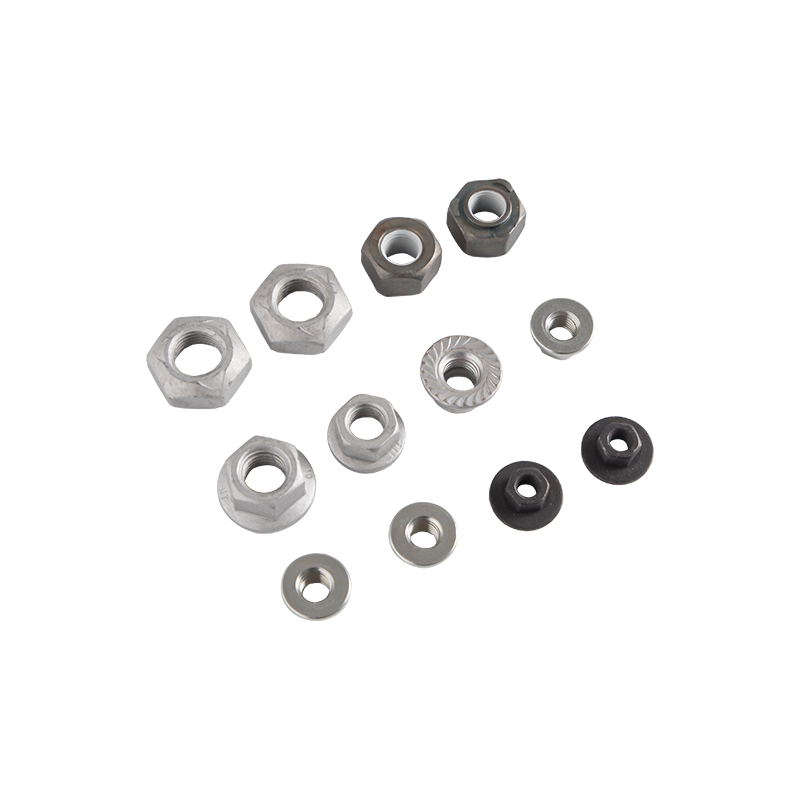
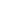| Article number | Product name | Size | Material | ||
| ZP | HDG | SS | |||
| 7710006 | T-type springless nut | M6 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710008 | T-type springless nut | M8 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710010 | T-type springless nut | M10 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710012 | T-type springless nut | M15 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710016 | T-type springless nut | M16 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710007 | T-type springless nut | 1/4 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710009 | T-type springless nut | 5/16 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710011 | T-type springless nut | 3/8 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710013 | T-type springless nut | 1/2 | ● | ● | ● |
| 7710017 | T-type springless nut | 5/8 | ● | ● | ● |
Welcome to Jiaxing Taigor Machinery Co., Ltd.

-
Home +
- About us +
-
Products +
Bolt and Nuts Screw nut DM6A4692 Bolts DM6A4728 Auto Part Bolts Auto Parts Bolts Multi-Purpose Construction Bolts Spring washer Flange nuts Hex nuts Flat washers Long hex nutPunch and Dies Shaped K tube Shaped K tube Special-shaped push tube, punch Shaped K tube Shaped K tube Non-standard bottom plug Non-standard die Trimming die Multilayer Punch Shaped punch Shaped punch Special-shaped tool holder
-
Service +
- News +
-
Contact +
 中文简体
中文简体
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Deutsch
Deutsch